并发编程 从并发编程的视角了解 Go 高性能的本质
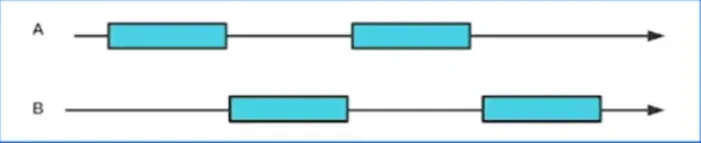
并发 VS 并行
并发:多线程程序在一个核的 CPU 上运行
并行:多线程程序在多个核的 CPU 上运行
Go 可以充分发挥多核优势,高效运行(高并发)
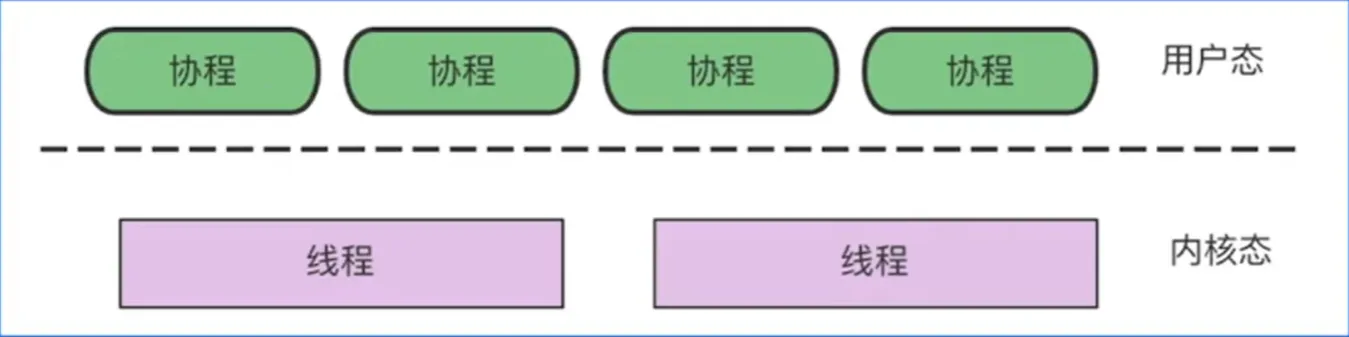
协程 Goroutine
协程:用户态,轻量级线程,栈 KB 级别
线程:内核态,线程跑多个协程,栈 MB 级别
快速 打印 hello goroutine : 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 func hello (i int ) println ("hello goroutine : " + fmt.Sprint(i)) } func HelloGoRoutine () for i := 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ { go func (j int ) hello(j) }(i) } time.Sleep(time.Second) }
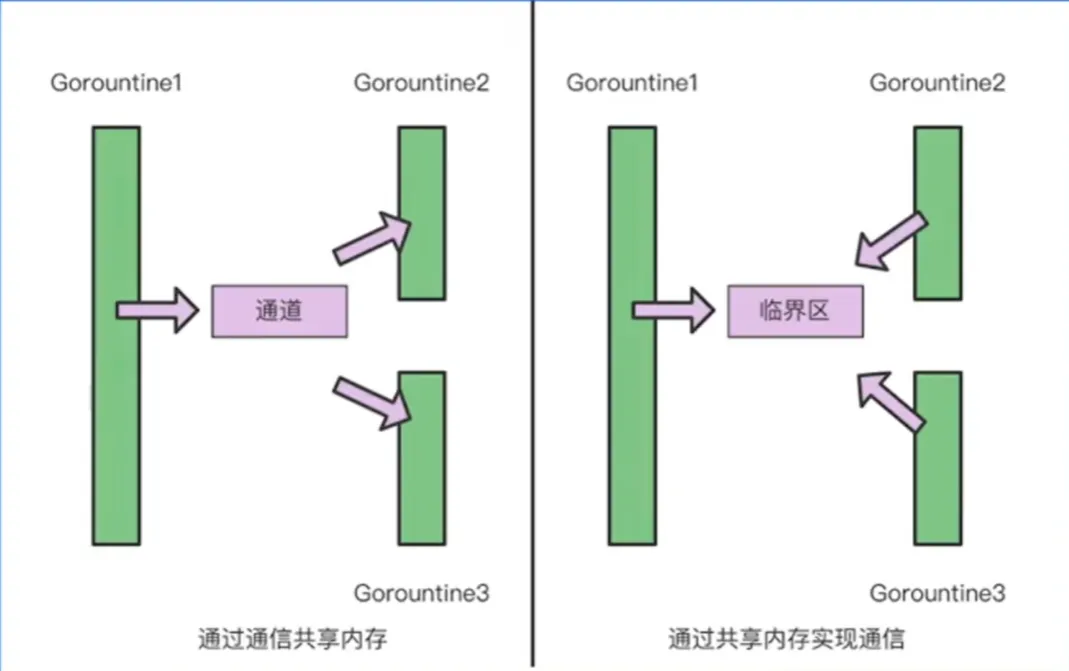
CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes)
通道 Channal
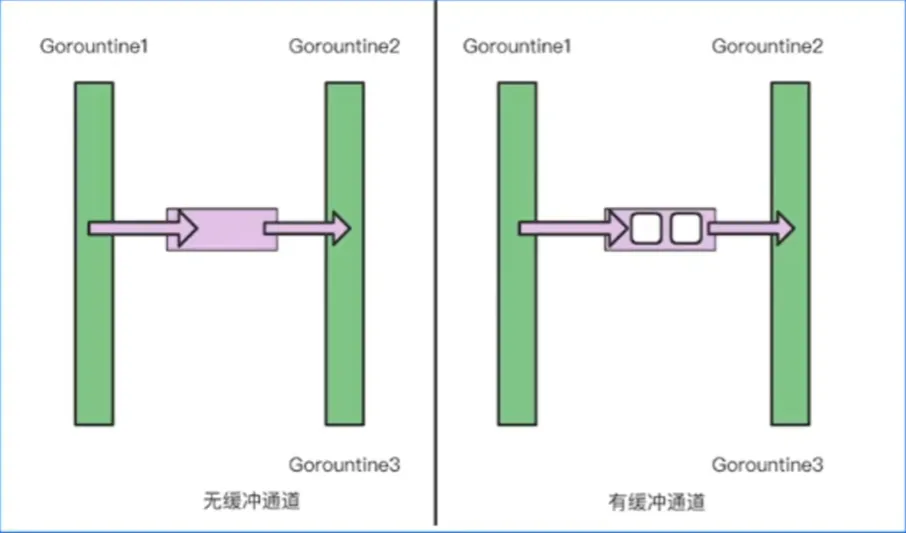
make(chan 元素类型,[缓冲大小])无缓冲通道 make(chan int)
有缓冲通道 make(chan int,2)
前者直接传输,也称为同构通道;后者类似快递柜,如果满了需要取走才能继续放,生产消费模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 func CalSquare () src := make (chan int ) dest := make (chan int , 3 ) go func () defer close (src) for i := 0 ; i < 10 ; i++ { src <- i } }() go func () defer close (dest) for i := range src { dest <- i * i } }() for i := range dest { println (i) } }
Sync 对变量进行 2000 次+1 操作,5 个协程并发执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 var ( x int64 lock sync.Mutex ) func addWithLock () for i := 0 ; i < 2000 ; i++ { lock.Lock() x += 1 lock.Unlock() } } func addWithoutLock () for i := 0 ; i < 2000 ; i++ { x += 1 } } func Add () x = 0 for i := 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ { go addWithoutLock() } time.Sleep(time.Second) println ("WithoutLock:" , x) x = 0 for i := 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ { go addWithLock() } time.Sleep(time.Second) println ("WithLock:" , x) }
使用time.Sleep()等待子协程全部结束不够优雅
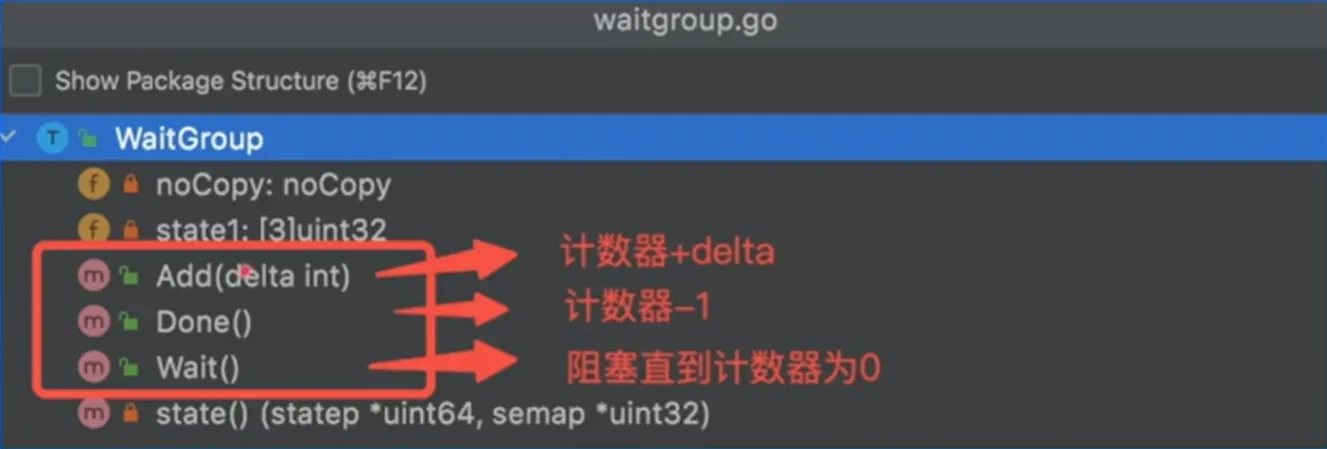
计数器:开启协程+1;执行结束-1;主协程阻塞知道计数器为 0
使用 WaitGroup 将 Goroutine 例子中的time.Sleep()替换优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 func hello (i int ) println ("hello goroutine : " + fmt.Sprint(i)) } func ManyGoWait () var wg sync.WaitGroup wg.Add(5 ) for i := 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ { go func (j int ) defer wg.Done() hello(j) }(i) } wg.Wait() }
依赖管理 了解 Go 语言依赖管理的演进路线
背景
工程项目不可能基于标准库 0~1 编码搭建
管理依赖库
Go 依赖管理演进
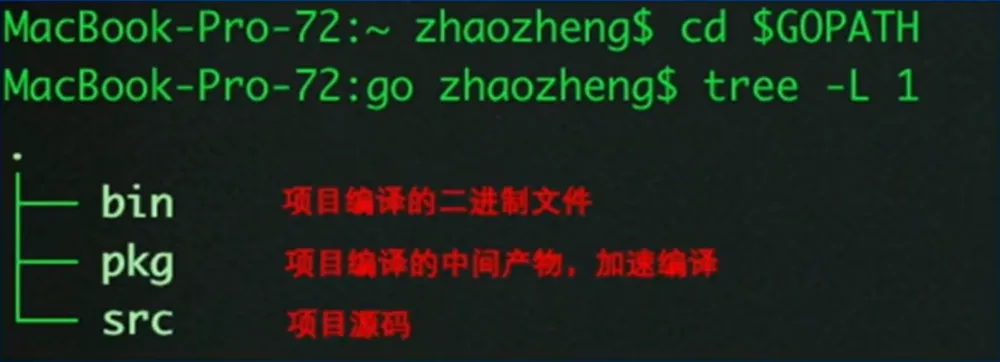
GOPATH
环境变量$GOPATH
项目代码直接依赖 src 下的源码
go get 下载最新版本的包到 src 目录下
弊端
场景:A 和 B 依赖于某一 package 的不同版本
问题:无法实现 package 的多版本控制
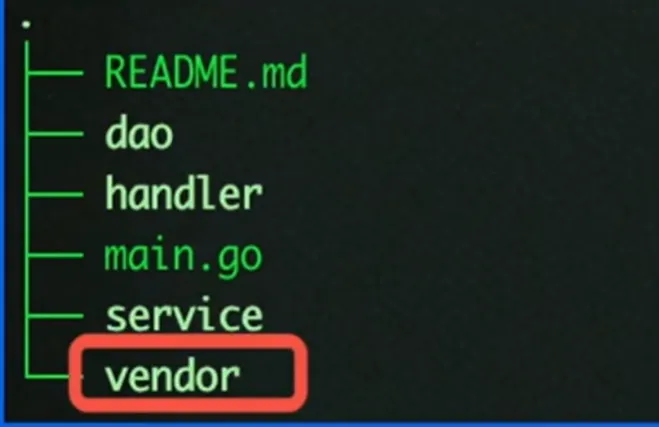
Go Vender
通过每个项目引入一份依赖的副本,解决了多个项目需要同一个 package 依赖冲突的问题
项目目录下增加 vender 文件,所有依赖包副本形式放在$ProjectRoot/vender
依赖寻址方式:vender => GOPATH
弊端
无法控制依赖的版本
更新项目又可能出现依赖冲突,导致编译出错
通过 go.mod 文件管理依赖包版本
通过 go get/go mod 指令工具管理依赖包
终极目标:定义版本规则和管理项目依赖关系
依赖管理三要素
配置文件,描述依赖 go.mod
中心仓库管理依赖库 Proxy
本地工具 go get/mod
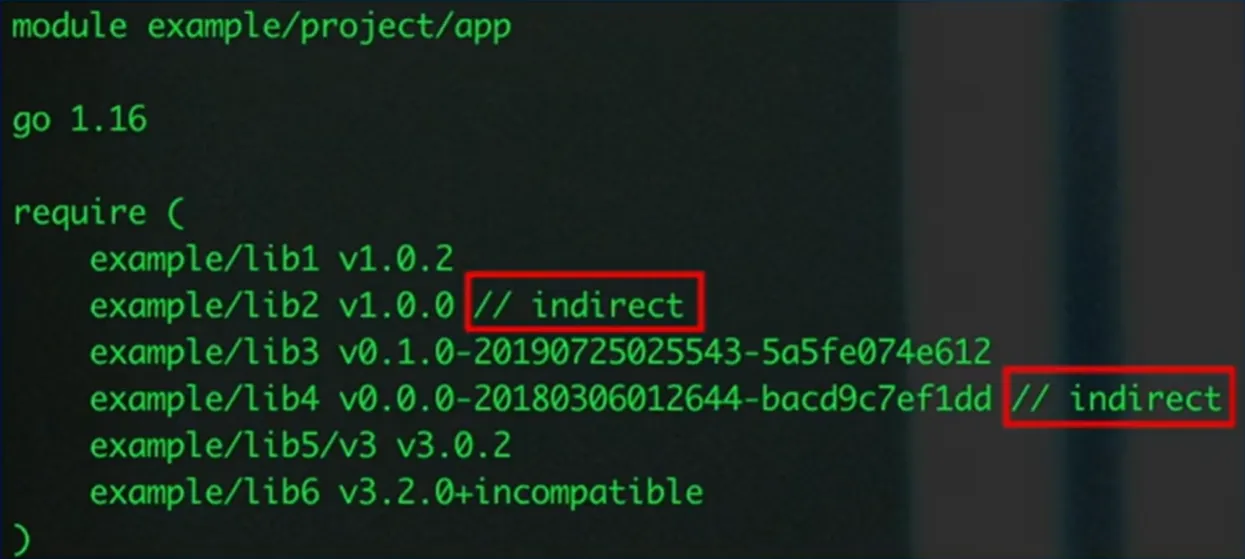
依赖配置-go.mod
依赖标识:[Module Path][Version/Pseudo-version
依赖配置-version
语义化版本
${MAJOR}.${MINOR}.${PATCH}V1.3.0
V2.3.0
基于 commit 伪版本
vX.0.0-yyyymmddhhmmss-abcdefg1234v0.0.0-20220401081311-c38fb59326b7
v1.0.0-20201130134442-10cb98267c6c
依赖配置-indirect
依赖配置-incompatible
主版本 2+模块会在模块路径增加/vN 后缀
对于没有 go.mod 文件并且主版本 2+的依赖,会+incompatible
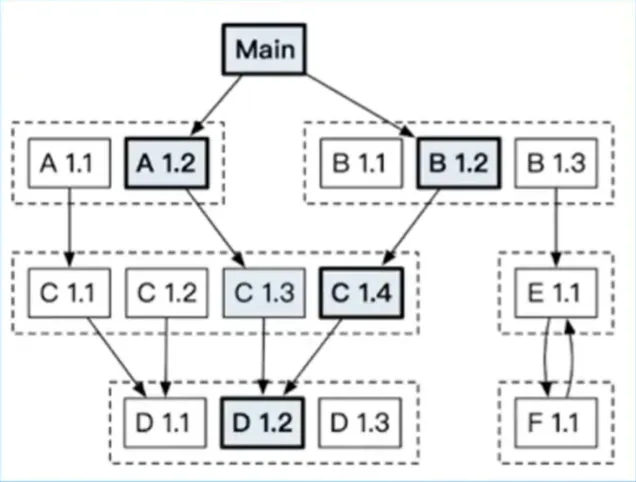
依赖配置-依赖图
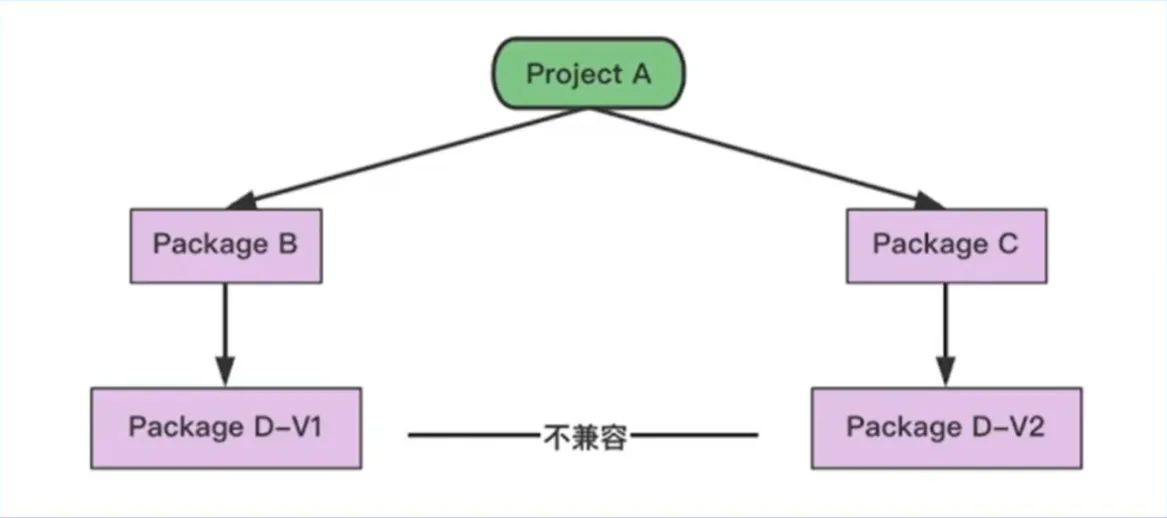
如果 X 项目依赖了 A、B 两个项目,且 A、B 分别依赖了 C 项目的 v1.3、v1.4 两个版本,最终编译时所使用的 C 项目的版本为如下哪个选项?(单选)
A.v1.3 B.v1.4 C.A 用到 C 时用 v1.3 编译,B 用到 C 时用 v1.4 编译
答案:B 选择最低兼容版本 (如果 C 项目有 v1.5 版本但未依赖,依旧选择 v1.4,即使都兼容)
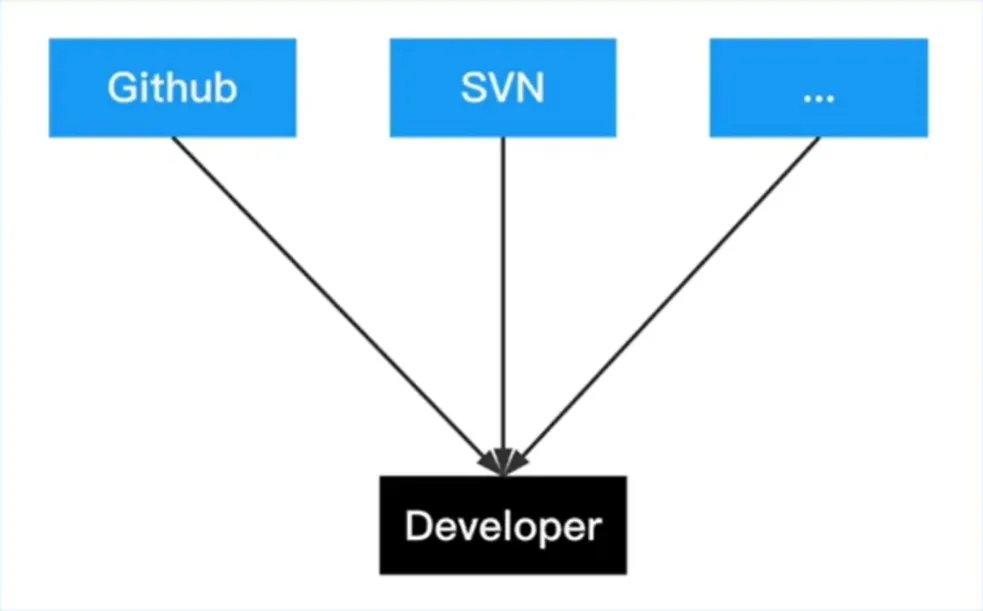
依赖分发-回源
依赖分发:依赖从其他地方获取
问题
无法保证构建稳定性
无法保证依赖可用性
增加第三方压力
依赖分发-Proxy
Proxy:一个服务站点,缓存源站中的软件内容,不会改变版本,直接从 Proxy 拉取依赖
依赖分发-变量 GOPROXY
工具-go get
go get example.org/pkg
@update 默认
@none 删除依赖
@v1.1.2 tag 版本,语义版本
@23dfdd5 特定的 commit
@master 分支的最新 commit
工具-go mod
go mod
init 初始化,创建 go.mod 文件
download 下载模块到本地缓存
tidy 增加需要的依赖,删除不需要的依赖
测试
回归测试 –> 集成测试 –> 单元测试
覆盖率逐层变大,成本却逐层降低
从单元测试实践出发,提高质量意识
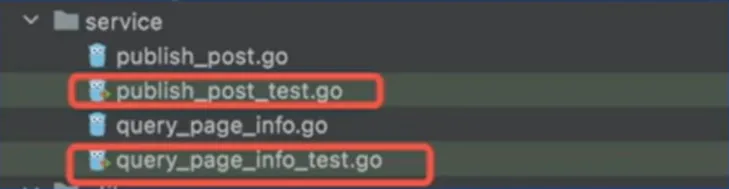
规则
所有测试文件以 _test.go 结尾
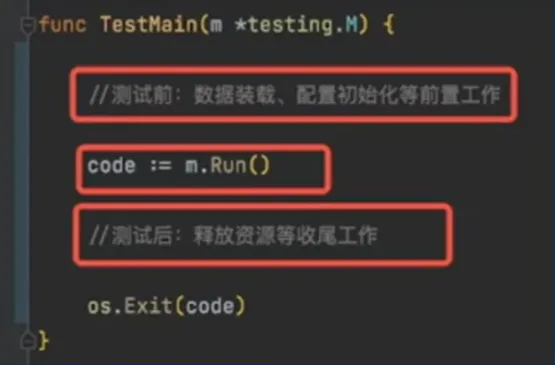
func TestXxx(*testing.T)初始化逻辑放到 TestMain 中
例子 print.go
1 2 3 4 5 package testfunc HelloTom () string { return "Tom" }
print_test.go
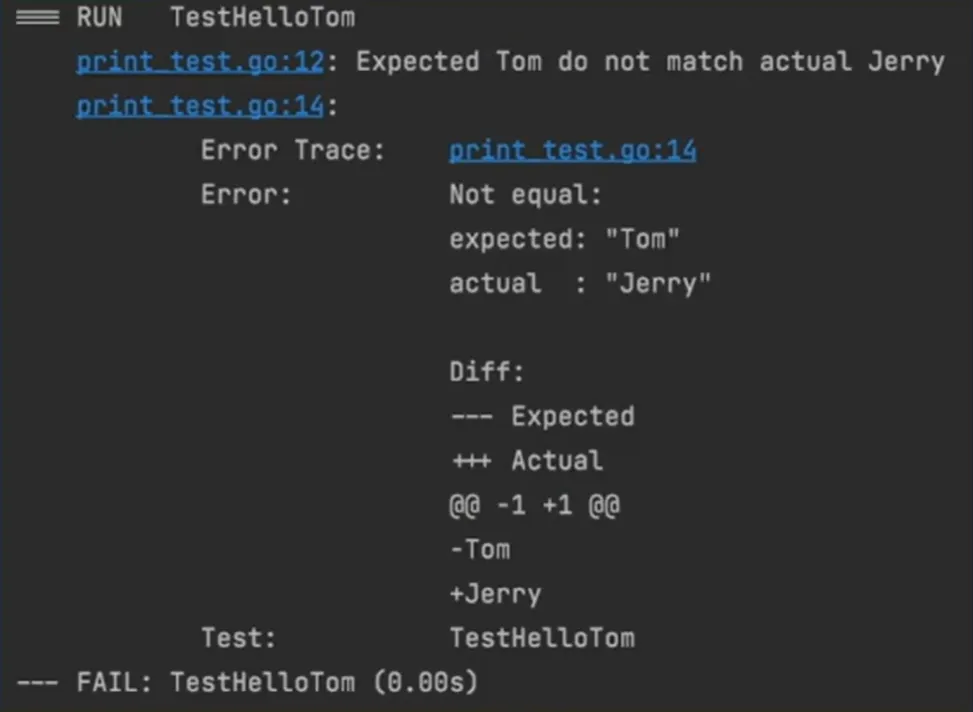
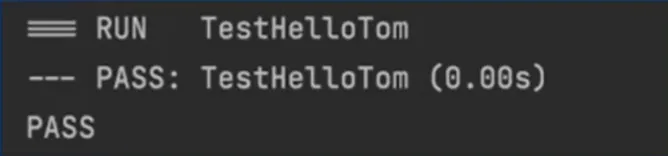
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package testimport ( "testing" ) func TestHelloTom (t *testing.T) output := HelloTom() expectOutput := "Tom" if output != expectOutput { t.Errorf("Expected %s do not match actual %s" , expectOutput, output) } }
运行 go test [flags][packages]
assert print.go
1 2 3 4 5 package testfunc HelloTom () string { return "Tom" }
print_test.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package testimport ( "testing" "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert" ) func TestHelloTom (t *testing.T) output := HelloTom() expectOutput := "Tom" assert.Equal(t, expectOutput, output) }
覆盖率
获取覆盖率需要在结尾加 --cover
go test judgment_test.go judgment.go --cover
judgment.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package testfunc JudgePassLine (score int16 ) bool { if score >= 60 { return true } return false }
不全 judgment_test.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package testimport ( "testing" "github.com/go-playground/assert/v2" ) func TestJudgePassLineTrue (t *testing.T) isPass := JudgePassLine(70 ) assert.Equal(t, true , isPass) }
测试函数没有测试到return false,因此只有 2/3 覆盖率
全 judgment_test.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package testimport ( "testing" "github.com/go-playground/assert/v2" ) func TestJudgePassLineTrue (t *testing.T) isPass := JudgePassLine(70 ) assert.Equal(t, true , isPass) } func TestJudgePassLineFail (t *testing.T) isPass := JudgePassLine(50 ) assert.Equal(t, false , isPass) }
tips
一般覆盖率:50%~60%,较高覆盖率 80%+
测试分支相互独立、全面覆盖
测试单元粒度足够小,函数单一职责
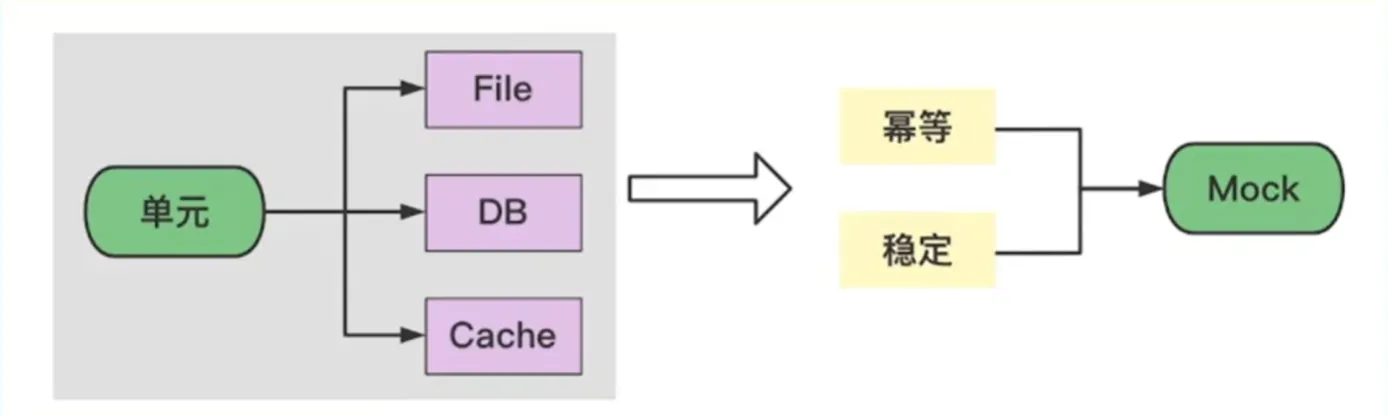
依赖
文件处理
mock.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package testimport ( "bufio" "os" "strings" ) func ReadFirstLine () string { open, err := os.Open("log" ) defer open.Close() if err != nil { return "" } scanner := bufio.NewScanner(open) for scanner.Scan() { return scanner.Text() } return "" } func ProcessFirstLine () string { line := ReadFirstLine() destline := strings.ReplaceAll(line, "ll" , "00" ) return destline }
mock_test.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package testimport ( "testing" "github.com/go-playground/assert/v2" ) func TestProcessFirstLine (t *testing.T) firstLine := ProcessFirstLine() assert.Equal(t, "line00" , firstLine) }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 func Patch (target, replacement interface {}) t := reflect.ValueOf(target) r := reflect.ValueOf(replacement) patchValue(t, r) return &PatchGuard{t, r} } func Unpatch (target interface {}) bool { return unpatchValue(reflect.ValueOf(target)) }
对 ReadFirstLine(文件处理代码)打桩测试,不再依赖本地文件
mock_test.go
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package testimport ( "testing" "bou.ke/monkey" "github.com/go-playground/assert/v2" ) func TestProcessFirstLineWithMock (t *testing.T) monkey.Patch(ReadFirstLine, func () string { return "line110" }) defer monkey.Unpatch(ReadFirstLine) line := ProcessFirstLine() assert.Equal(t, "line000" , line) }
优化代码,需要对当前代码分析
内置的测试框架提供了基准测试的能力
例子 随机选择执行服务器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package benchmarkimport ( "math/rand" "github.com/bytedance/gopkg/lang/fastrand" ) var ServerIndex [10 ]int func InitServerIndex () for i := 0 ; i < 10 ; i++ { ServerIndex[i] = i + 100 } } func Select () int { return ServerIndex[rand.Intn(10 )] }
运行 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 func BenchmarkSelect (b *testing.B) InitServerIndex() b.ResetTimer() for i := 0 ; i < b.N; i++ { Select() } } func BenchmarkSelectParallel (b *testing.B) InitServerIndex() b.ResetTimer() b.RunParallel(func (pb *testing.PB) for pb.Next() { Select() } }) }
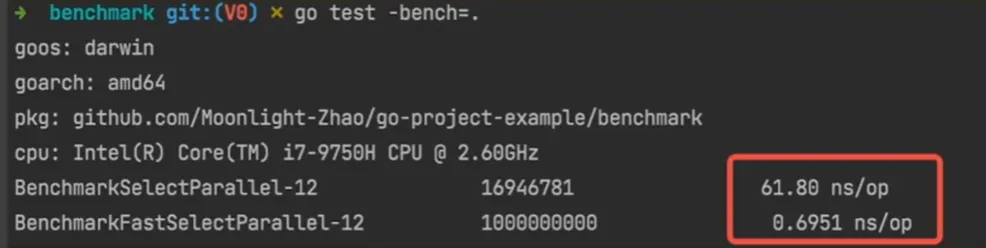
并行做基准测试性能会有劣化,rand 函数为了保证全局的随机性和并发安全有一把全局锁,在一定程度上降低了并发的性能
优化 1 2 3 func FastSelect () int { return ServerIndex[fastrand.Intn(10 )] }
项目实战 通过项目需求、需求拆解、逻辑设计、代码实现感受真实的项目开发
需求背景(需求模型来源) 青训营话题页forum.juejin.cn/youthcamp/p…
需求描述
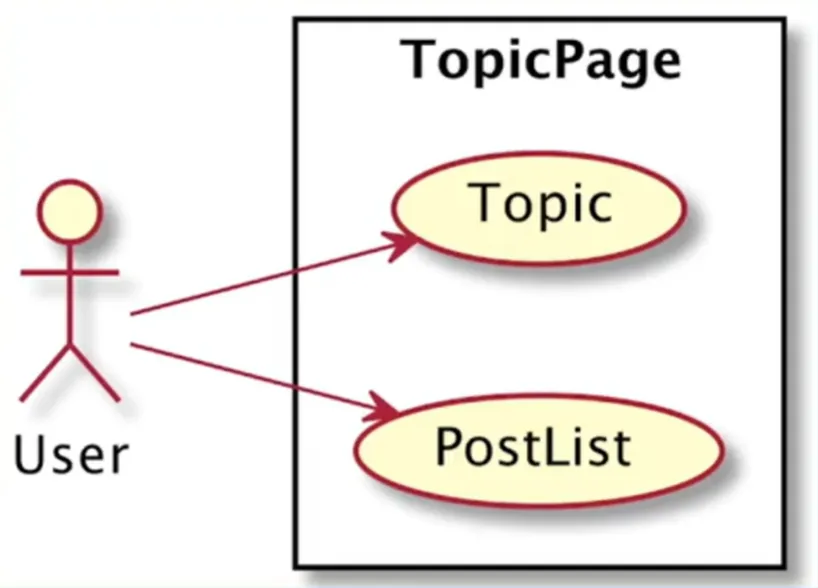
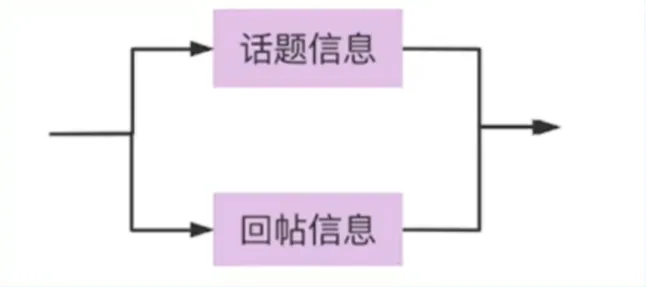
社区话题页面
展示话题(标题,文字描述)和回帖列表
暂不考虑前端页面实现,仅仅实现一个本地 web 服务
话题和回帖数据用文件存储
需求用例
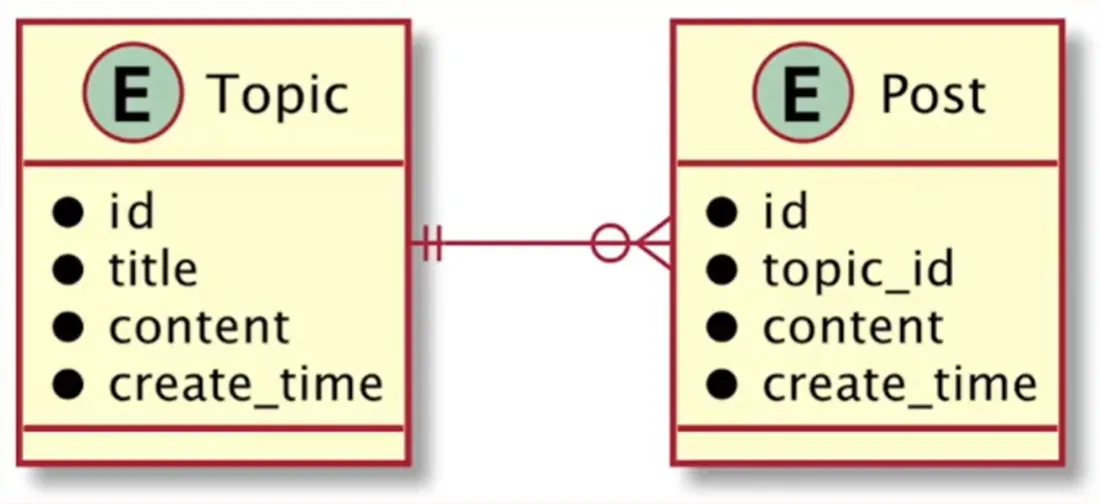
ER 图-Entity Relationship Diagram
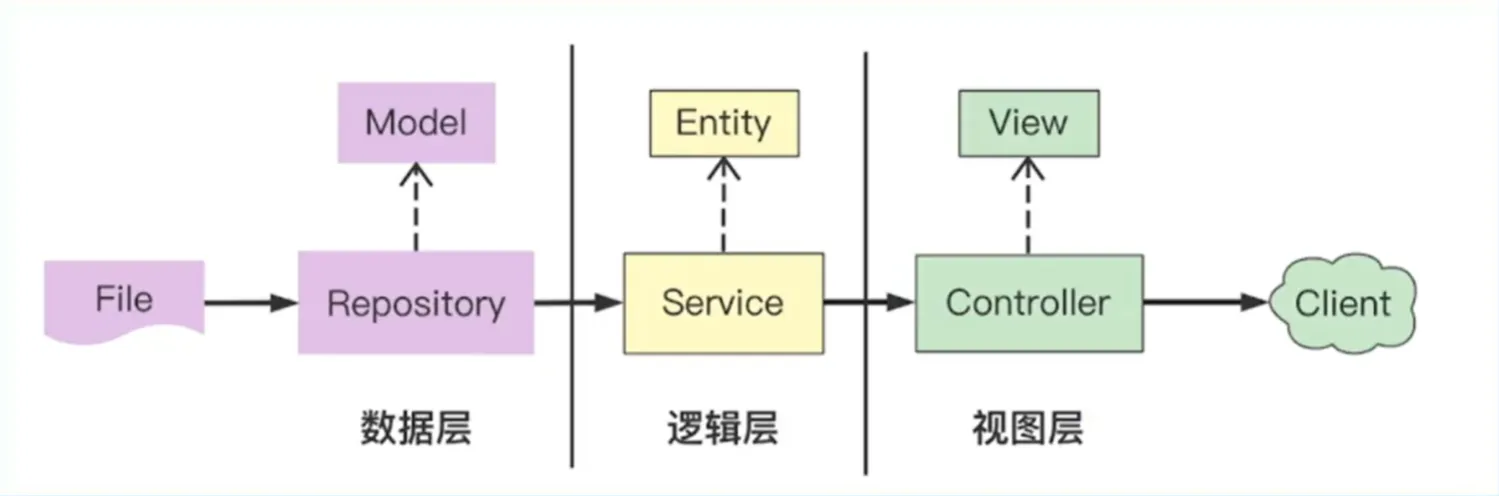
分层结构
数据层:数据 Model,外部数据的增删改查
逻辑层:业务 Entity,处理核心业务逻辑输出
视图层:视图 View,处理和外部的交互逻辑
组件工具
Repository
实现查询
QueryTopicById
QueryPostsByParentId
index
1 2 3 4 var ( topicIndexMap map [int64 ]*Topic postIndexMap map [int64 ][]*Post )
初始化话题数据索引(帖子略)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 func initTopicIndexMap (filePath string ) error { open, err := os.Open(filePath + "topic" ) if err != nil { return err } scanner := bufio.NewScanner(open) topicTmpMap := make (map [int64 ]*Topic) for scanner.Scan() { text := scanner.Text() var topic Topic if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte (text), &topic); err != nil { return err } topicTmpMap[topic.Id] = &topic } topicIndexMap = topicTmpMap return nil }
查询
话题查询(帖子略)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 type Topic struct { Id int64 `json:"id"` Title string `json:"title"` Content string `json:"content"` CreateTime int64 `json:"create_time"` } type TopicDao struct {} var ( topicDao *TopicDao topicOnce sync.Once ) func NewTopicDaoInstance () topicOnce.Do( func () topicDao = &TopicDao{} }) return topicDao } func (*TopicDao) int64 ) *Topic { return topicIndexMap[id] }
Service 实体 1 2 3 4 type PageInfo struct { Topic *repository.Topic PostList []*repository.Post }
流程
代码流程编排 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 func (f *QueryPageInfoFlow) error ) { if err := f.checkParam(); err != nil { return nil , err } if err := f.prepareInfo(); err != nil { return nil , err } if err := f.packPageInfo(); err != nil { return nil , err } return f.pageInfo, nil }
可用性 并行处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 func (f *QueryPageInfoFlow) error { var wg sync.WaitGroup wg.Add(2 ) go func () defer wg.Done() topic := repository.NewTopicDaoInstance().QueryTopicById(f.topicId) f.topic = topic }() go func () defer wg.Done() posts := repository.NewPostDaoInstance().QueryPostsByParentId(f.topicId) f.posts = posts }() wg.Wait() return nil }
Controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 type PageData struct { Code int64 `json:"code"` Msg string `json:"msg"` Data interface {} `json:"data"` } func QueryPageInfo (topicIdStr string ) topicId, err := strconv.ParseInt(topicIdStr, 10 , 64 ) if err != nil { return &PageData{ Code: -1 , Msg: err.Error(), } } pageInfo, err := service.QueryPageInfo(topicId) if err != nil { return &PageData{ Code: -1 , Msg: err.Error(), } } return &PageData{ Code: 0 , Msg: "success" , Data: pageInfo, } }
Router
初始化数据索引
初始化引擎配置
构建路由
启动服务
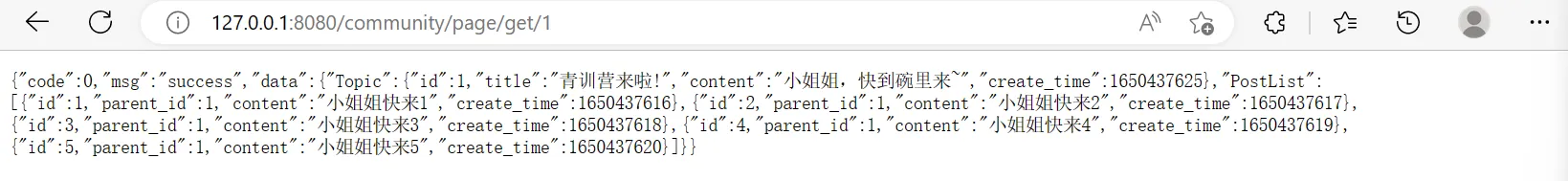
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 func main () if err := Init("./data/" ); err != nil { os.Exit(-1 ) } r := gin.Default() r.GET("/community/page/get/:id" , func (c *gin.Context) topicId := c.Param("id" ) data := cotroller.QueryPageInfo(topicId) c.JSON(200 , data) }) err := r.Run() if err != nil { return } }
运行
课后实践
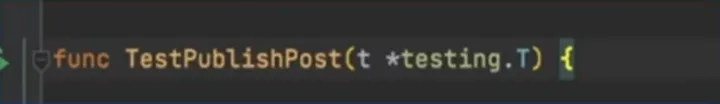
支持发布帖子
支持 Id 生成需要保证不重复、唯一性
Append 文件,更新索引,注意 Map 的并发安全问题